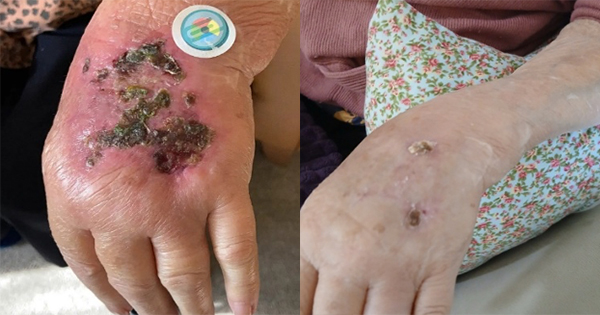
This article discusses how a community wound healing clinic (WHC) was implemented within one locality in an NHS community healthcare organisation to address key clinical challenges, such as variations in wound care practice and the implementation of evidence-based care. To ensure consistency in care, an evidence-based clinical pathway was introduced, which included the UrgoStart treatment range of dressings that has been recommended for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE, 2019a) as it is associated with enhanced wound healing when used in addition to standard care. A standardised referral pathway from the General Practitioner to the WHC was also introduced. In total, 33 patients (34 wounds) with a wide range of wound types and co-morbidities were involved in the clinical evaluation. The findings demonstrate realworld outcomes that concur with findings from the CHALLENGE (Meaume et al, 2012) and EXPLORER (Edmonds et al, 2018) randomised controlled trials and are further endorsement of how NICE recommendations translate into tangible improvements when combined with an evidence-based approach.