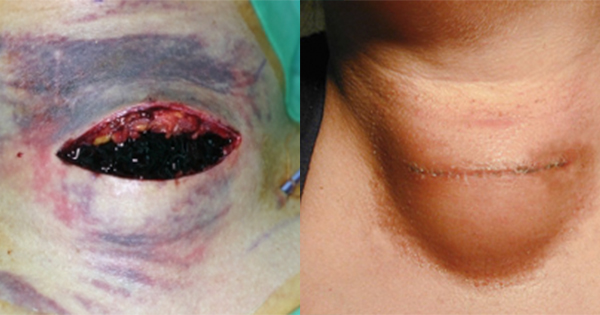
Background: Understanding the burden of surgical site infection (SSI) requires comprehensive, reliable and comparable data. However, many hospitals do not routinely collect information on wound healing after the patient leaves hospital. Aim: To evaluate five post-discharge surveillance strategies that collect patient/carer reported outcomes on wound healing following adult and paediatric surgery. Method: Between March 2020 and February 2021, colleagues from five specialist hospitals in England collaborated to collect baseline and compliance data for the different methods of postdischarge surveillance. The five methods included were telephone follow-up; postal questionnaires; postal questionnaires and contacting non-responders by telephone to asking patients to install a postoperative app on their personal smartphone (Medopad, Huma) and using a SSI surveillance text link, which did not need to be installed (Isla, Islacare Ltd). Results: Overall, 1432 patients out of 2116 patients provided information about their wound after discharge. The group of patients who were asked to install an app on their smart device had the lowest return rate for information on their wound, while the system that used a text link and did not need to be installed had one of the highest return rates. Conclusion: Understanding baseline practice and evaluating different methods of discharge surveillance may help to drive improvement in this area. Our early findings suggest that in practice, a SSI surveillance approach using a text link and photos, such as Isla, which is used in hospital before discharge by staff and postdischarge by patients warrants further attention.