The emergence of mpox, a rare infection usually found in central and western Africa, is increasing worldwide. Although there has been an increase in mpox infections in the UK, the risk remains low. Mpox can spread through close skin-to-skin and intimate contact (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 2022). The illness normally lasts two to four weeks and symptoms include fever, chills, muscle aches, headache, cough, sneezing and a rash that can appear around various areas of the body including the chest, hands, face, mouth, genitals and anus (CDC, 2022). The rash can turn into small, painful and infectious fluid-filled blisters, contact with the contents of which can result in viral transmission (CDC, 2022; NHS, 2022). Blisters normally scab and fall off. Infected persons may experience some or all of the above symptoms. Symptoms may appear up to three weeks after exposure.
There is no definitive treatment for mpox, however, most persons infected will recover within a few weeks. In the UK, the Modified Vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) smallpox vaccine has been offered and has been suggested to give a good level of immune protection against mpox (NHS, 2022) and is currently being rolled out globally. In the US, the CDC recommends an antiviral therapy, tecovirimat, for people who are immunocompromised and who are more likely to get severely ill (CDC, 2022). There are various ongoing trials testing treatment for mpox (National Institute for Health and Care Research, 2022).
A unique antimicrobial, antiviral and antifungal treatment currently being used in clinical practice to treat various types of wounds and skin irritations includes medical grade honey, due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, enhanced rate of healing, deodorising action, reduction in oedema and debriding actions. (Molan, 2009; Molan, 2011; Seckam and Cooper, 2013; Vandamme et al, 2013).
Methods
Medihoney® barrier cream (MHBC) is indicated for reducing skin breakdown caused by incontinence and radiation treatment and has been used in case reports to treat atopic eczema (Seckam and Turkos, 2014). The cream can be applied in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions and is beneficial in maintenance of skin integrity caused by shear and friction, while maintaining the skin’s pH. This case study demonstrates the results seen with twice-daily applications of MHBC to an mpox blister.
The affected area was cleaned with saline twice daily before an application of a pea-sized amount of MHBC. The blister was covered with a standard dressing after the day application and left open after the evening application.
Ethical considerations and consent
Ethical approval for the case study was granted from the Cardiff School of Sport and Health Sciences under the Cardiff Metropolitan University Ethics Framework (Sta-9249). Consent was obtained accordingly for anonymised pictures and quotes for this case study.
Results
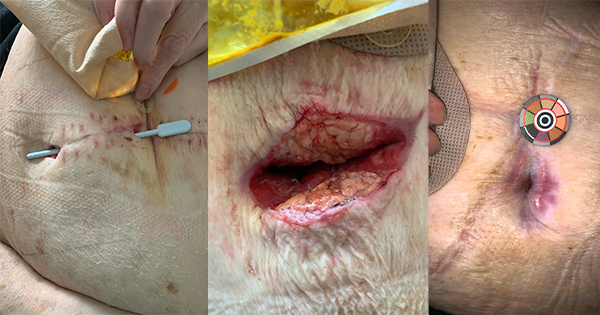
A 38-year-old male patient presented with a mpox blister to the inner left thigh (diagnosed by a PCR test on a viral swab taken from the blister opening) and was treated with MHBC. Patch testing after 24 hours was performed before treatment twice daily to the blister.
Discussion
This case study highlights positive outcomes seen with the usage of MHBC to treat an mpox blister. Although some patients do not experience symptoms that require treatment, in this case study the patient noted that the application of MHBC helped to heal the blister and reduce inflammation and irritation. Effective symptom management of painful itchy lesions might help reduce the risk of transmission from scratching or picking at infectious lesions. The use of MHBC, in this case, suggests some potential benefits for treating mpox blisters and possible reduction of transmission risk by ameliorating provocative symptoms. Further studies exploring the biological, physiological mechanisms and psychosocial implications of this disease is recommended.
Conclusion
A patient with an mpox blister experienced relief of symptoms, itching, decreased inflammation and improved skin conditions after 1 month of twice-daily applications of MHBC.
We believe such conservative management holds promise to help reduce transmission risk while also providing symptomatic relief and that further research is warranted.